Structure in C
What is Structure
Structure in c is a user-defined data type that enables us to store the collection of different data types. Each element of a structure is called a member. Structures ca; simulate the use of classes and templates as it can store various information
The ,struct keyword is used to define the structure. Let's see the syntax to define the structure in c.
cstruct StructureName {
// Member variables or fields DataType1 member1; DataType2 member2; // ... DataTypeN memberN; };Here's a brief explanation of the terms used in the syntax:
1. struct: Keyword used to define a structure.
2. StructureName: The name you give to the structure type.
3. DataType1, DataType2, ..., DataTypeN: The data types of the individual members or fields of the structure.
Here's an example using a simple structure to represent a point in 2D space:
c#include <stdio.h> // Define a structure named 'Point' struct Point {
int x;int y; };int main() { // Declare a variable of type 'struct Point'
struct Point p1; // Assign values to the members of the structure p1.x = 10; p1.y = 5;// Display the information printf("Coordinates: (%d, %d)\n", p1.x, p1.y); return 0; }In this example, the structure Point has two members, x and y, both of type int. The main function demonstrates how to declare a variable of type struct Point, assign values to its members, and then use those values.
The following image shows the memory allocation of the structure employee that is defined in the above example.
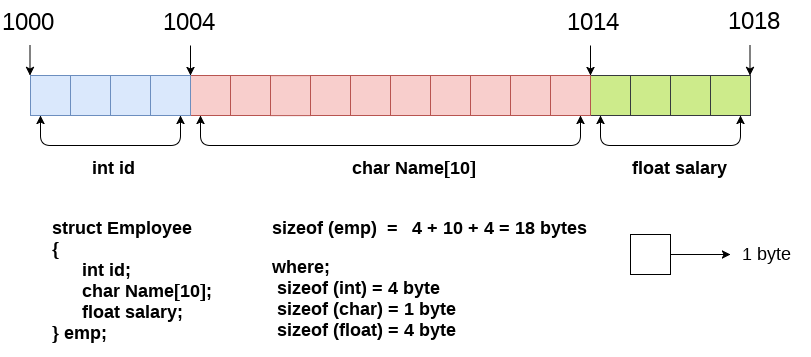
Here, struct is the keyword; employee is the name of the structure; id, name, and salary are the members or fields of the structure. Let's understand it by the diagram given below:

Why use structure?
In C, there are cases where we need to store multiple attributes of an entity. It is not necessary that an entity has all the information of one type only. It can have different attributes of different data types. For example, an entity Student may have its name (string), roll number (int), marks (float). To store such type of information regarding an entity student, we have the following approaches::
c#include <stdio.h> // Define a structure named 'Person'
struct Person { char name[50]; int age; float height; }; int main() { // Declare a variable of type 'struct Person' struct Person person1; // Access and assign values to the members of the structure strcpy(person1.name, "John Doe"); person1.age = 25; person1.height = 5.9; // Display the information printf("Name: %s\n", person1.name); printf("Age: %d\n", person1.age); printf("Height: %.2f\n", person1.height);return 0; }In this example, a structure named Person is defined with three members: name (an array of characters), age (an integer), and height (a floating-point number). In the main function, a variable person1 of type struct Person is declared and then filled with data.
Structures in C are particularly useful when you want to model real-world entities with multiple attributes or properties. They provide a way to organize and manipulate data in a more structured manner.
Declaring structure variable
To declare a variable of a structure type in C, you follow this general syntax:
cstruct StructureName variableName;Here's an example using the previously defined Point structure::
c#include <stdio.h> // Define a structure named 'Point' struct Point {
int x; int y; }; int main() { // Declare a variable of type 'struct Point' struct Point p1; // Assign values to the members of the structure
p1.x = 10; p1.y = 5; // Display the information
printf("Coordinates: (%d, %d)\n", p1.x, p1.y); return 0; }In this example, struct Point p1; declares a variable named p1 of type struct Point. After declaring the variable, you can access and modify its members (x and y) using the dot (.) operator.
You can also initialize the structure variable at the time of declaration, like this:
cstruct Point p1 = {10, 5};This initializes the x member of p1 to 10 and the y member to 5.
Which approach is good
If number of variables are not fixed, use the 1st approach. It provides you the flexibility to declare the structure variable many times.
If no. of variables are fixed, use 2nd approach. It saves your code to declare a variable in main() function.
Accessing members of the structure
There are two ways to access structure members:
By . (member or dot operator)
By -> (structure pointer operator)
Structure in C example
Let's see a simple example of structure in C language.
c#include <stdio.h> // Define a structure named 'Person'
struct Person {
char name[50]; int age; float height; }; int main() { // Declare a variable of type 'struct Person' struct Person person1; // Assign values to the members of the structure strcpy(person1.name, "John Doe"); person1.age = 25; person1.height = 5.9; // Display the information printf("Name: %s\n", person1.name); printf("Age: %d\n", person1.age); printf("Height: %.2f\n", person1.height); return 0; } Output::
makefileName: John Doe
Age: 25
Height: 5.90This program defines a structure Person, creates an instance of it (person1), assigns values to its members, and then prints out the information. The output reflects the values assigned to the structure members during initialization.


.png)
.png)
.png)

0 Comments